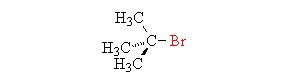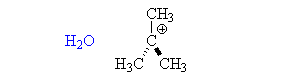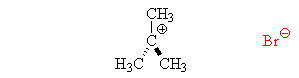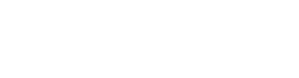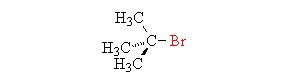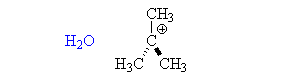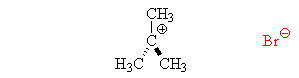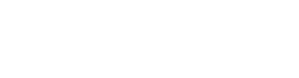The SN1 reaction
The SN1 reaction is a two-step reaction in which
- The leaving group leaves, forming a carbocation. This is the slow step, and so the rate is dependent only on the concentration of the substrate.
- The nucleophile attacks the carbocation. It can do this from either side, typically in a 50/50 ratio. Therefore about half the product has retained the original configuration, and about half is inverted.
- Protonated nucleophiles, such as methanol, then lose a proton to the solvent.
Click to see this diagrammed.
Reaction animation:
animated GIF